41 under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?
Secondary Deviance: Definition & Examples - Simply Sociology Secondary deviance refers to the deviant identity or career that results after the deviant activity is recognized by society, and the perpetrator is formally labeled as deviant. This is distinct from primary deviance, deviant behavior that occurs unlabelled. Sociology Exam 2 Flashcards | Quizlet a.when the deviant label is internalized b.when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people c.when the deviant label is applied later in life d.when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful a.when the deviant label is internalized A gay man joins a dating website.
Underwhatcircumstancesdoesadeviantlabelleadfromprimary - Course Hero when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is internalized d. when the deviant label is applied later in life e. when the deviant label concerns a very minor type of deviance ANS: C NOT: Factual e ) when the deviant label is internalized

Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?
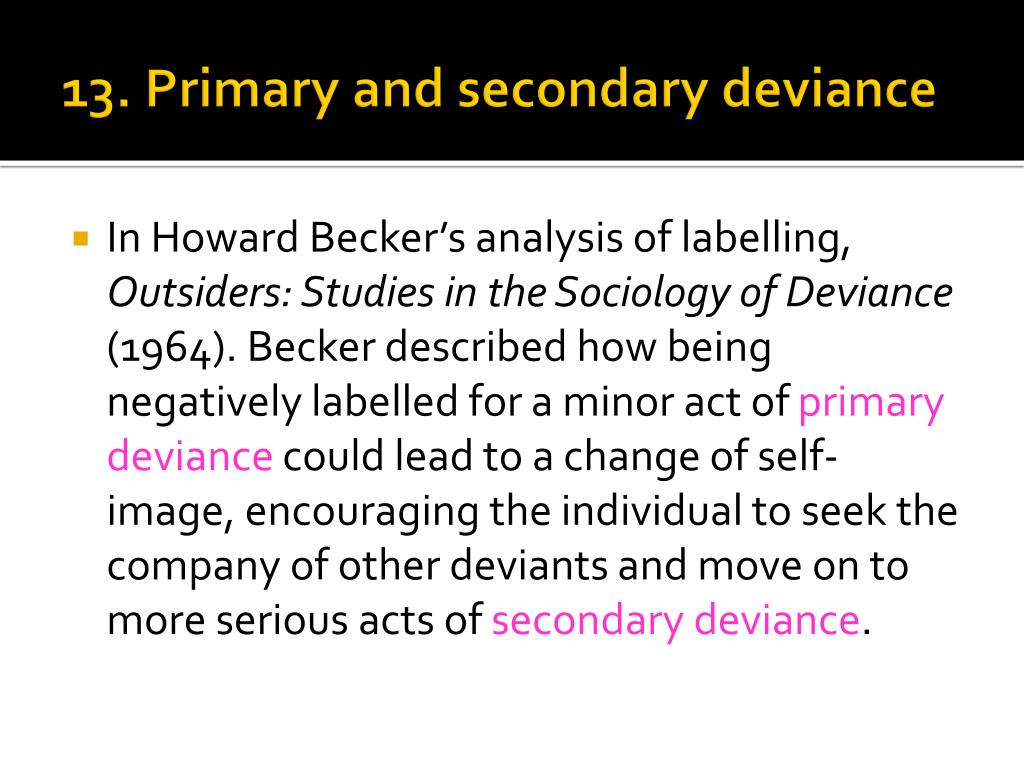
18. Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to ... Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is internalized d. when the deviant label is applied later in life Perspectives on deviance: Differential association, labeling theory ... Society's reaction to and its labels for the deviant behavior and the person who committed the deviant behavior are very important. An act labeled as primary deviance does not have huge consequenceS. This act produces very little societal push back. The reaction to the deviant behavior is very mild and, and doesn't affect the person's self esteem. Labeling Theory of Deviance: Definition & Examples Primary and Secondary Deviance. Labeling theory stresses the idea that deviance is a relative term. Under this perspective, people become deviant not because of the act itself, but how people ...
Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?. The Labeling Theory Of Deviance - 190 Words - Internet Public Library Primary deviance is the act itself then secondary deviance occurs if the label from primary deviance sticks. The taking on a deviant identity by talking, acting, or dressing in a different way, rejecting the people who are critical, and repeatedly breaking the rules. Secondary Deviance: Definition & Examples - Study.com This diagram shows how reactions to deviant behavior can lead to either primary or secondary deviance. In reaction 1, the deviant behavior receives a mild corrective punishment that has no long ... Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to ... The circumstance that can lead a deviant label from primary to secondary deviance is when the deviant label is applied later in life What is labelling theory? According to the labeling hypothesis, the terminology used to define or categorize people may determine or have an impact on their behavior and sense of self. under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to ... Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applies by a large number of people to that individual b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is accepted by the individual and seen as deviant d. when the deviant label is applied ...
Sociology 200 Chapter 6 Flashcards | Quizlet when the deviant label is accepted as part of one's identity Deviance occurs in all cultures and is impossible to completely get rid of in society. True The FBI's Uniform Crime Report (UCR) measures all crime reported in the United States through eight different types of crime separated into two categories. False 7.2 Theoretical Perspectives on Deviance and Crime - OpenStax As a result, the student starts acting out even more and breaking more rules; the student has adopted the "troublemaker" label and embraced this deviant identity. Secondary deviance can be so strong that it bestows a master status on an individual. A master status is a label that describes the chief characteristic of an individual. Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead - Course Hero 49. Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is accepted by the individual d. when the deviant label is applied later in life ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: Page 157 Labeling theory | Concepts, Theories, & Criticism | Britannica Secondary deviance, however, is deviance that occurs as a response to society's reaction and labeling of the individual engaging in the behaviour as deviant.This type of deviance, unlike primary deviance, has major implications for a person's status and relationships in society and is a direct result of the internalization of the deviant label. . This pathway from primary deviance to ...
Labeling Theory of Deviance: Definition & Examples Primary and Secondary Deviance. Labeling theory stresses the idea that deviance is a relative term. Under this perspective, people become deviant not because of the act itself, but how people ... Perspectives on deviance: Differential association, labeling theory ... Society's reaction to and its labels for the deviant behavior and the person who committed the deviant behavior are very important. An act labeled as primary deviance does not have huge consequenceS. This act produces very little societal push back. The reaction to the deviant behavior is very mild and, and doesn't affect the person's self esteem. 18. Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to ... Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is internalized d. when the deviant label is applied later in life
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-104821085-58b88efd3df78c353cc1fb17.jpg)

































Post a Comment for "41 under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?"